Embracing Eco Design: How Modular Garments and Accessories Lead to a Circular Economy
Garments and accessories are often complex composites, made from various materials to meet distinct requirements. For example, shoes consist of a rubber sole paired with an upper made of leather or fabric. Tailor-made suits feature horsehair reinforcements in the front and lapel, combining wool exteriors with silk, viscose, or nylon linings. Winter jackets are filled with feathers, sandwiched between water-repellent fabric and synthetic linings.
For end-of-life treatments, these composite products present challenges. Each material requires a unique recycling process. To maintain the quality of recycled materials, components like the rubber sole of a shoe must be separated from the leather or fabric upper. This principle applies to all composite garments. Each material must be separated to ensure it can be reused in its pure, high-quality form.
Unfortunately, most apparel is not designed for easy disassembly. Disassembling different materials currently requires a labor-intensive and manual process. Consequently, “recycled” garments and accessories are often shredded into a low-quality textile mixture. Effective recycling and repair are virtually nonexistent.
To truly implement a circular economy and protect our future prosperity, we must consider product structures and hierarchy. Effective repair, remanufacturing, and recycling demand that garments and accessories be modular. Achieving this necessary modularity involves using reversible joining methods and prioritizing design for disassembly.
Resortecs is at the forefront of this revolution, providing design-for-disassembly solutions that enable high-quality textile recycling on an industrial scale. By pioneering innovative threads and disassembly techniques, Resortecs empowers brands, sorters, and recyclers to address today’s environmental challenges at the pace and scale the Earth needs.
Resortecs combines thermal engineering, eco-design, and chemical engineering to offer state-of-the-art solutions that empower the entire textile value chain to close the loop. Discover Smart Stitch™ and Smart Disassembly™: Resortecs’ solution for multi-material disassembly in a fast, easy, and cost-efficient manner. To learn more about the financial impact of design for disassembly, dive into the From Waste to Profit report.
Smart Stitch™ is a range of 16 heat-dissolvable threads – enabling automatic thermal disassembly and design for recycling. Suitable for a variety of applications, from apparel to fire-resistant workwear, the Smart Stitch™ threads have been exhaustively tested on various production line configurations and are compatible with every stitching machine widely available on the market.
Smart Disassembly™ is the world’s first thermal disassembly system – combining the quality of manual methods with the speed of mechanical processes. A fully automatic process empowering sorters and recyclers to disassemble textile products while removing zippers, elastic bands, and any other trims that hinders recycling 5x faster than manual disassembly. The low-oxygen chamber ensures no risks of fabric oxidation and recyclability rates as high as 90%.
When you hear “circular economy,” think “modular.” This shift in perspective is essential for fostering sustainable fashion and advancing circular design principles.
Photo by Ethan Bodnar on Unsplash
The importance of yields in scaling industrial textile-to-textile recycling.

Textile recycling and circularity are becoming crucial points to be addressed for the survival of the textile industry. The surge in urgency in recent years is facilitated by the increasingly tightening regulations on handling textiles at end-of-life and the mandatory use of recycled content, as well as changing demands from critical stakeholders such as investors, media, and end-users.
In the discussions around closing the loop for the textile industry, one thing remains hidden: technology alone will not be enough. To make post-consumer textile-to-textile recycling the new norm, it needs to become profitable. And work is still required to achieve that profitability by scaling processes and increasing their efficiencies. Without tackling the low yield of current textile-to-textile recycling supply chains, recycling feedstock capacity and profit margins for textile players will remain at risk. This poses a bigger concern on achieving a closed loop at an European level, compromising EU’s future competitiveness in the market.
Big strides have been achieved in reaching the required recycled feedstock levels, yet innovative recycling technologies alone are not sufficient. Textile-to-textile recycling must evolve to be both financially viable and operationally scalable.
“Textile-to-textile recycling must evolve to be both financially viable and operationally scalable.”
When industrialising new processes, a key metric to consider is the productivity and efficiencies – i.e. yields. As argued in the study ‘The Economics of Yield-Driven Processes’ by Roger E. Bohn and Christian Terwiesch, the economic performance of production processes is heavily influenced by process yields, as these have a substantial impact on product cost, gross revenue and contribution margin. According to research on the hard disk drive (HDD) industry, the report states: “A three percentage point increase in yields can be worth about 6% of gross revenue and 17% of contribution. In fact, an eight percentage point improvement in process yields can outweigh a US$20/h increase in direct labour wages”.
In textile recycling, the level of contamination or the purity of feedstock has the most pronounced impact on yields. Some contaminations, such as elastane, are completely blocking the majority of mechanical and chemical recycling processes, while others are simply classified as waste, directly increasing overall process costs.
With 78% of apparel composed of various components, the pressing question arises: which pre-processing method maximises efficiency to achieve high yields throughout the process?
On average, trims represent 10-20% of the garment weight. Mechanical removal of trims from the textiles, also called mechanical disassembly, results in the loss up to 60% of the garment (depending on the desired output purity requirements). Manual disassembly fares slightly better, but still incurs losses ranging around 40%. For a deeper dive into the cost analysis of textile disassembly processes, refer to Resortecs’ From Waste to Profit report.
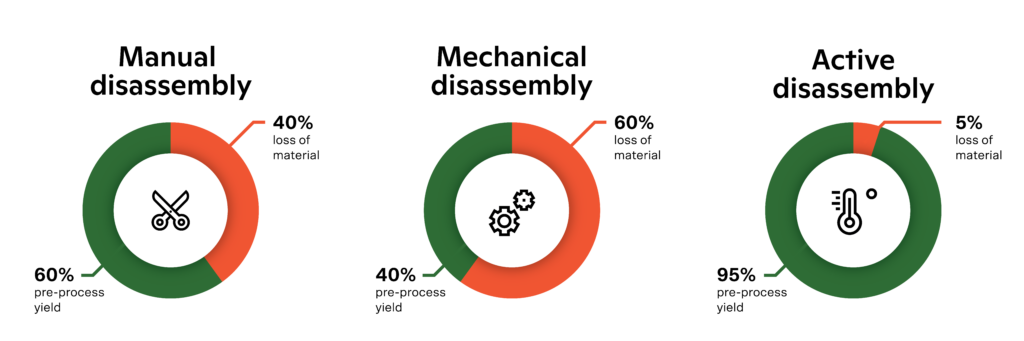
Those pre-processing yields, combined with the average yield of 80% from chemical recycling processes result in an overall post-consumer textile-to-textile recycling process with yields as low as 32%. This strikingly low yield metric underscores that price competitive recycled materials will take time to materialise. It is unsurprising that post-consumer textile-to-textile recycled materials remain costly, and why recycled PET bottles (which bypass the need for disassembly or component sorting) continue to dominate as the most popular recycled material source in the textile industry. As Leachman documented in 1996 with the Berkeley project on HDD manufacturing, a yield rate of 50% effectively doubles the costs per unit compared to those at a 100% yield.
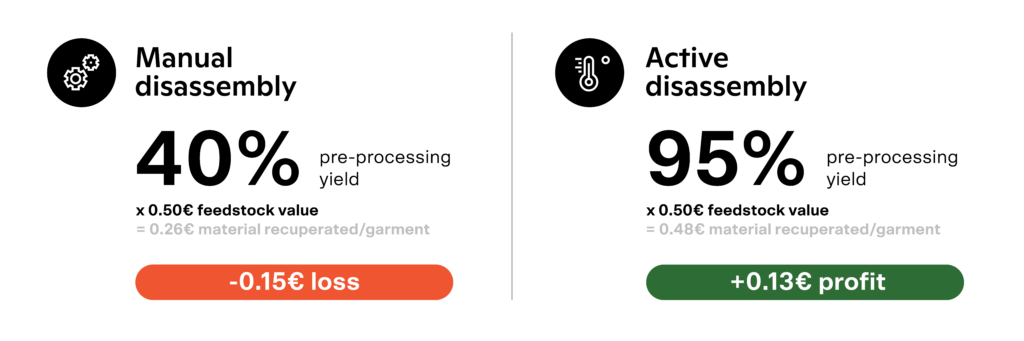
With eco-design solutions such as Resortecs, the disassembly or “de-stitching” of garments is automated, allowing for the elimination of trims and the separation of two different textiles in reusable fractions with an average material recuperation rate of 95%. This pre-processing technology not only facilitates the recycling of complex/multilayer textile products, such as denim, jackets and swimwear, but also roughly doubles the post-consumer textile recycling yields.
Despite the widespread recognition of the crucial role yields play, it is surprising how little emphasis is placed on discussions regarding efficiencies and productivity at annual textile circularity and recycling conferences. Similar to the semiconductor industry in the 1990s, prioritising yields is imperative when deciding on which technologies and processes to integrate. By increasing the pre-processing and recycling yields we will be able to industrialise textile-to-textile recycling and achieve price-competitive sustainable materials for the textile industry.
In conclusion, the journey towards mainstream textile-to-textile recycling hinges on maximising process yields and optimising efficiency across the value chain. As described above, an optimised eco-design has a significant impact on the recycling process yields and thus largely affects the price of recycled content textile brands have to pay to be compliant. This insight highlights an opportunity for textile players to switch from a reactive to proactive approach: brands must take action in the way their garments are designed to ensure low price recycled feedstock, leading to less compromise on their margins in the long-term.
By addressing pre-processing challenges and leveraging eco-design technologies like Resortecs, the industry can pave the way for price-competitive sustainable materials and drive the transition towards a circular economy in the textile sector.
Author: Cédric Vanhoeck, CEO at Resortecs
Join us.
Subscribe to our newsletter.
By subscribing, I agree with having my personal data stored and processed by Resortecs so I can receive future updates and marketing offers.
