Resortecs Study: Estimate on the achievable target for recycled content in textile products
As the global community continues to grapple with the urgent need for sustainable solutions, the textile industry stands at a critical crossroads. With increasing awareness of environmental degradation and resource depletion, there is a growing imperative to reevaluate traditional manufacturing practices and embrace more sustainable alternatives. At the forefront of this movement is the concept of eco-design, which emphasizes the integration of environmental considerations into product development processes.
As the European Union discusses the EU Ecodesign Directive and other measures to boost textile circularity, it is clear that the environmental impact of textile products has made fashion one of the region’s top priorities in the circular transition. On average, an EU citizen consumes 26 kg of textile and generates 11 kg of waste each year. Yet only 1% of the material used in textile production is recycled — the remaining 99% is landfilled or incinerated.
Objective
In alignment with the principles of eco-design for sustainable products (ESPR), this study seeks to estimate the achievable target for recycled content in textile products, specifically apparel, that are placed on the European market. The focus is on utilizing recycled content sourced from collected textile waste within Europe over the next decade.
By leveraging recycled materials, manufacturers can reduce reliance on virgin resources, minimize waste generation, and mitigate the environmental footprint of their products. Through a comprehensive analysis of industry trends, consumer preferences, and regulatory frameworks, this report aims to provide insights and recommendations for establishing meaningful recycled content targets that promote sustainability without compromising product quality or performance.
Methodology
The study aimed to assess the potential feedstock available from collected textile waste in Europe, both with and without pre-recycling preparation such as disassembly. It investigated the amount of attainable feedstock achievable under current conditions, as well as the additional feedstock that could be obtained if pre-recycling preparation methods like disassembly were implemented.
The following assumptions were considered in the calculation:
• Global Market Size: The global market for textile products is estimated to consist of 116 billion pieces annually. Of these, the European market represents 28%, equivalent to 32.5 million pieces, with an average weight of 300g per piece, totaling 9744 tons per year. This value is assumed to remain stable over the study period despite the growth potential.
• Monomaterial Fraction: Currently, monomaterial products constitute 22% of total fashion collections. It is anticipated that this proportion will increase due to eco-design requirements (ESPR), reaching 30% by 2035.
• Composition of Materials: PET accounts for 12% of the material composition, while cotton represents 40%. The recycling efficiency is estimated at 47% for PET and 49% for cotton, accounting for material loss during recycling processes such as melt spinning, twining/spinning, weaving, and confection.
• Disruptors and Multimaterial Products: Products made from mono-materials and containing recycling disruptors such as zippers, labels, and buttons comprise 69% of total fashion pieces7. Multi Material products constitute 9% of the total fashion pieces7.
• Textile waste collection rate: The average textile collection rate in Europe is currently estimated at 38% with the aim of achieving 100% with the mandatory textile waste collection.
Data Analysis
In the light of the waste framework directive WFD EC 2008/98 and the mandatory collection of separated textile waste the percentage of the collection rate is expected to increase from the present state of 38% to 60% in 2027, up to 80% in 2030 and 100% by 2035.
The mono-material fraction currently constitutes around 22% of the total garments in the EU market. With the implementation of eco-design requirements and the potential for garments to be designed as mono-material, eliminating the need for trims or multi-material components to meet performance and durability standards, this fraction is projected to rise to 30% by 2035. Accordingly, given the current collection rate of 38% of textile waste in Europe, the textile industry can procure 98 tons of polyester feedstock and 326 tons of cotton feedstock in 2024.
This volume of feedstock will be adequate to meet the requirement for 4% recycled content in new garments without necessitating any modifications to current practices or additional investments. With the aim of achieving collection rates of up to 100% in the EU, the potential feedstock obtainable from mono-material textile waste collected in Europe is anticipated to amount to at least 346 tons of cotton feedstock and 1152 tons of polyester feedstock. This could potentially translate into achievable recycled content targets of 14% to 15% by 2035, respectively.
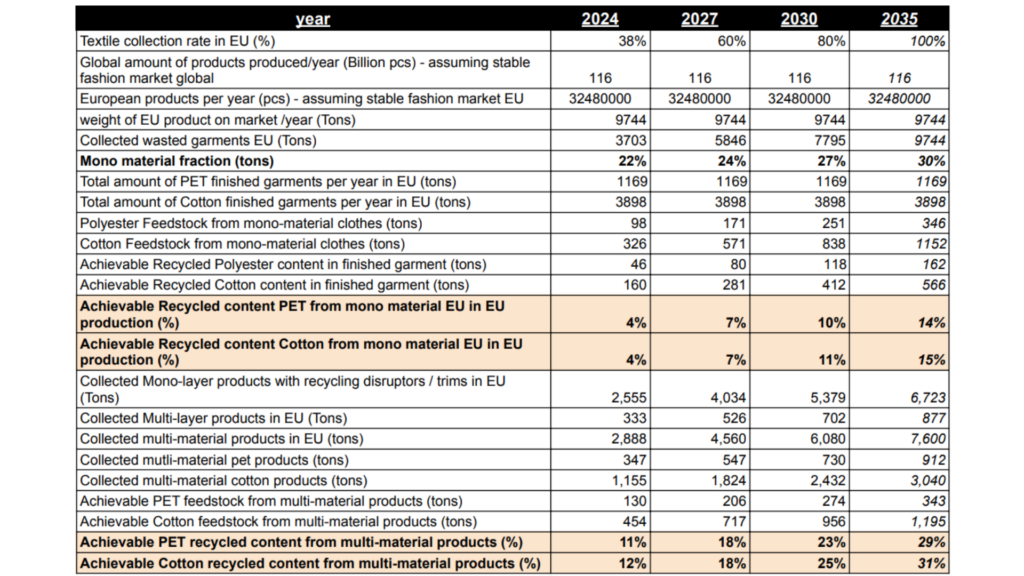
Table 1: Potential textile recycled content targets and their feasibility in the EU.
Tapping into multi-material textile products, which may consist of mono-material with recycling disruptors or multi-layer compositions, and assuming they are prepared for recycling through effective disassembly, the achievable PET feedstock is projected to increase from 130 tons in 2024 with a 38% collection rate to 343 tons in 2035 with a 100% textile waste collection rate. Consequently, the achievable PET recycled content from multi-material sources will range from g.
A similar trend is expected for cotton feedstock, estimated at 454 tons in 2024 and evolving to 1195 tons if 100% of multi-material apparel waste is collected and disassembled in Europe. This will result in achievable cotton recycled content ranging from 12% to 31%.
Combining the potential PET feedstock collected in Europe from both mono-material and multi material apparel products will result in 16% of achievable recycled PET target in 2024 with projection to increase to 45% by 2035, as demonstrated in Figure 1.
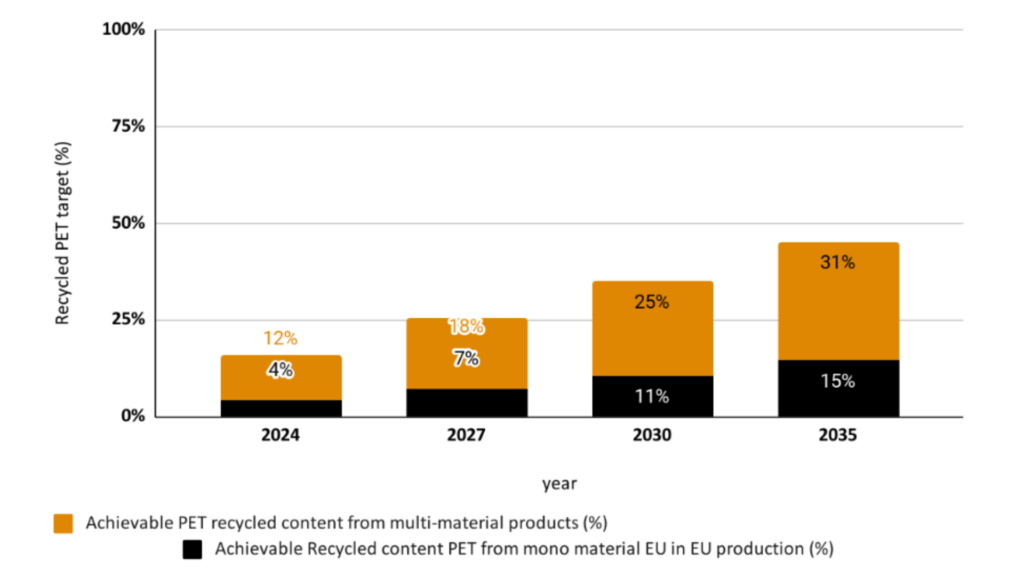
Figure 1: Achievable Recycled PET Content (%) from Mono-Material and Multi-Material Textile Waste Collected in the EU.
Combining the potential cotton feedstock collected in Europe from both mono-material and multi material apparel products will result in 39% of achievable recycled cotton target in 2024 with projection to increase to 43% by 2035, as demonstrated in Figure 2.
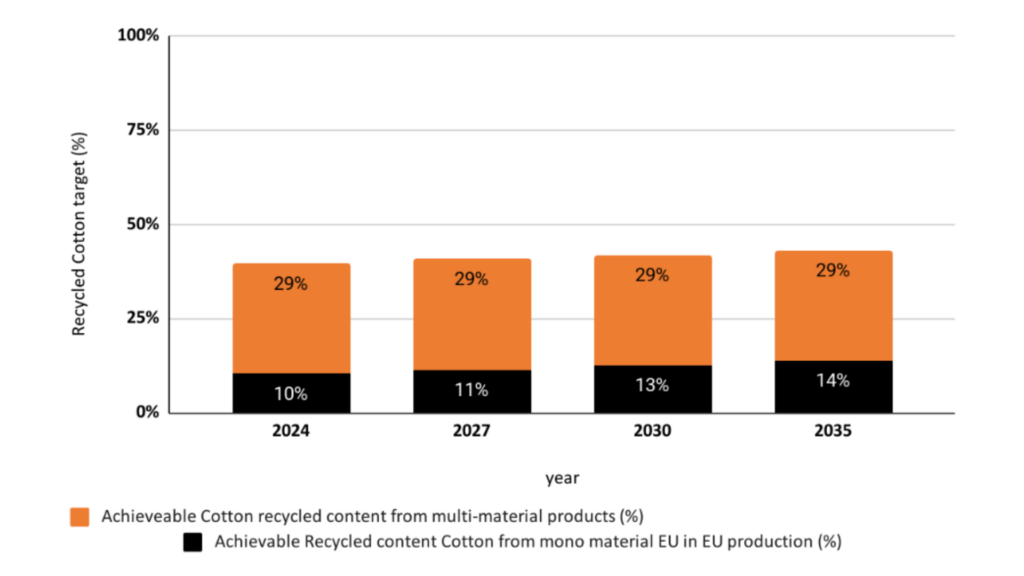
Figure 2: Achievable Recycled Cotton Content (%) from Mono-Material and Multi-Material Textile Waste Collected in the EU.
Conclusion
The study’s results underscore the tangible potential for achieving significant levels of recycled content in new apparel products. The min achievable recycled content target is 4% from mono-material garments without changing any current practices that could rise to 14% when 100% of textile collection rate is attained. By tapping into multi-material garments after preparation for recycling, a min achievable recycled content target is 11% with potential to rise to 31% when 100% of multi-material textile collection rate is attained. With careful management of current European textile waste, a realistic recycled content target of 15% is within reach. Looking ahead, as textile waste collection becomes mandatory and reaches 100% penetration over the next decade, the projected recycled content target could soar to an impressive 43%. It’s crucial to note that while market growth may amplify these volumes, our study prioritizes responsible production practices and expects products to have longer lifespans in the market, and it didn’t consider any market growth.
The study findings highlight the pivotal role of the disassembly process, exemplified by Resortecs’ design for disassembly solution. Effective preparation of products for recycling will unlock higher volumes of feedstock with the necessary purity for textile-to-textile recycling processes. This optimization not only streamlines the sorting process and increases recycling yields, but also generates financial benefits for sorters and recyclers. Moreover, it significantly mitigates environmental impact by reducing waste generation and curbing the need for new material sourcing. This emphasizes the imperative for defining eco-design requirements that foster an enabling environment for textile-to-textile recycling, thereby actualizing the waste hierarchy. Such an environment must prioritize pre-recycling techniques like disassembly and set ambitious recycled content targets that not only reflect high percentages but also ensure the origin of recycled content is sustainable and traceable. This holistic approach is essential for driving meaningful progress towards a circular and sustainable textile industry.
Sources
1. 2009/125/EC
2. Textiles in Europe’s circular economy, EEA, 19 Nov 2019.
3. A new textile economy: redesigning fashion’s future (Ellen MacArthur Foundation) – Circular Fibers Initiative analysis.
4. Statista – Apparel Europe, and Apparel Market Worldwide.
5. Global apparel market: The revenue of the global apparel market was calculated to amount to 1.53 trillion U.S. dollars in 2022 while Apparel – Europe: In 2023, the revenue in the Apparel market in Europe is estimated to be US$474.40bn hence the EU market share of the global apparel market is 28%.
6. Resortecs internal calculation for an average garment weight.
7. Refashion, Characterisation study of the incoming and outgoing streams from sorting facilities report, 2023.
8. Fashion For Good, Sorting for Circularity Report, 2022.
9. Recycling efficiency was estimated on analysis of current recycling technology and industrial discussions with developing recycling technologies at lower TRL.
10. EU exports of used textiles in Europe’s circular economy – Feb 2023.
11. European Directive ((EU) 2018/851) amending Directive 2008/98/EC
The Industry is Changing
The textile industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by various global factors. Climate change, tightening legislation, geopolitical tensions, resource depletion, and the de-globalization of trade are leading to a paradigm shift in business operations.
Discover Resortecs’ comprehensive guide on how textile players can navigate these challenges and take control of their value and supply chains to mitigate the industry’s most significant risks of the decade.
Key Risks Facing the Textile Industry
Risk 1: High Volatility of the Availability and Price of Natural Raw Materials
The availability and pricing of natural raw materials are becoming increasingly unpredictable due to climate change and resource depletion.
Risk 2: High Volatility of the Availability and Price of Recycled Material
Recycled materials are facing similar volatility issues, influenced by market demand, legislation, and sustainability practices.
Risk 3: Market Access Challenges
Geopolitical tensions and shifting trade policies are creating barriers to market access, impacting global supply chains.
Risk 4: Lead Time Issues Due to Logistical Perturbations and Disruptions
Logistical challenges, such as transportation delays and disruptions, are causing significant lead time issues, affecting the timely delivery of goods.
Risk 5: Costly EPR Fees
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) fees are increasing operational costs, necessitating efficient waste management and recycling processes.
Risk 6: Growth of Second-Hand C2C Channels
Increasing popularity of consumer-to-consumer (C2C) second-hand platforms
that propose a price competitive and sustainable offer.
Risk 7: Growth of Ultra-Fast Fashion
The rise of ultra-fast fashion brands offering extremely low prices is driving consumers away from higher priced more sustainable fashion products.
Take Control of Your Supply Chain
Brands need a comprehensive and systematic strategy to address these multifaceted risks, incorporating eco-design, design for disassembly, and circular economy practices as essential elements. Resortecs’ Smart Stitch™ and Smart Disassembly™ technologies enable efficient disassembly and recycling of textile products, allowing brands to reclaim double the amount of feedstock from discarded textiles up to 15 times faster and at the highest purity levels.
Proactively address the textile industry’s biggest risks with Resortecs’ advanced solutions. Achieve compliance, operational efficiency, and financial ROI through innovative technologies designed to enhance sustainability and streamline supply chains.

Click Here to Download the Full Guide
Gain deeper insights into how you can mitigate crucial risks in the textile industry by downloading Textile Sourcing & Market Access Risks.
Photo by Ethan Bodnar on Unsplash
The importance of yields in scaling industrial textile-to-textile recycling.

Textile recycling and circularity are becoming crucial points to be addressed for the survival of the textile industry. The surge in urgency in recent years is facilitated by the increasingly tightening regulations on handling textiles at end-of-life and the mandatory use of recycled content, as well as changing demands from critical stakeholders such as investors, media, and end-users.
In the discussions around closing the loop for the textile industry, one thing remains hidden: technology alone will not be enough. To make post-consumer textile-to-textile recycling the new norm, it needs to become profitable. And work is still required to achieve that profitability by scaling processes and increasing their efficiencies. Without tackling the low yield of current textile-to-textile recycling supply chains, recycling feedstock capacity and profit margins for textile players will remain at risk. This poses a bigger concern on achieving a closed loop at an European level, compromising EU’s future competitiveness in the market.
Big strides have been achieved in reaching the required recycled feedstock levels, yet innovative recycling technologies alone are not sufficient. Textile-to-textile recycling must evolve to be both financially viable and operationally scalable.
“Textile-to-textile recycling must evolve to be both financially viable and operationally scalable.”
When industrialising new processes, a key metric to consider is the productivity and efficiencies – i.e. yields. As argued in the study ‘The Economics of Yield-Driven Processes’ by Roger E. Bohn and Christian Terwiesch, the economic performance of production processes is heavily influenced by process yields, as these have a substantial impact on product cost, gross revenue and contribution margin. According to research on the hard disk drive (HDD) industry, the report states: “A three percentage point increase in yields can be worth about 6% of gross revenue and 17% of contribution. In fact, an eight percentage point improvement in process yields can outweigh a US$20/h increase in direct labour wages”.
In textile recycling, the level of contamination or the purity of feedstock has the most pronounced impact on yields. Some contaminations, such as elastane, are completely blocking the majority of mechanical and chemical recycling processes, while others are simply classified as waste, directly increasing overall process costs.
With 78% of apparel composed of various components, the pressing question arises: which pre-processing method maximises efficiency to achieve high yields throughout the process?
On average, trims represent 10-20% of the garment weight. Mechanical removal of trims from the textiles, also called mechanical disassembly, results in the loss up to 60% of the garment (depending on the desired output purity requirements). Manual disassembly fares slightly better, but still incurs losses ranging around 40%. For a deeper dive into the cost analysis of textile disassembly processes, refer to Resortecs’ From Waste to Profit report.
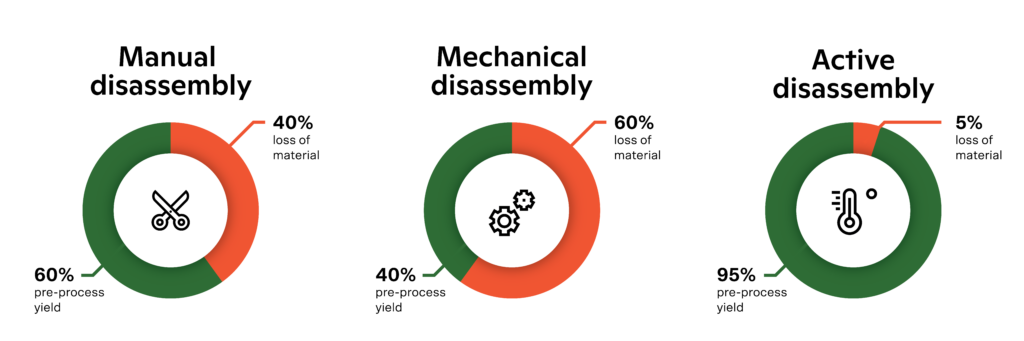
Those pre-processing yields, combined with the average yield of 80% from chemical recycling processes result in an overall post-consumer textile-to-textile recycling process with yields as low as 32%. This strikingly low yield metric underscores that price competitive recycled materials will take time to materialise. It is unsurprising that post-consumer textile-to-textile recycled materials remain costly, and why recycled PET bottles (which bypass the need for disassembly or component sorting) continue to dominate as the most popular recycled material source in the textile industry. As Leachman documented in 1996 with the Berkeley project on HDD manufacturing, a yield rate of 50% effectively doubles the costs per unit compared to those at a 100% yield.
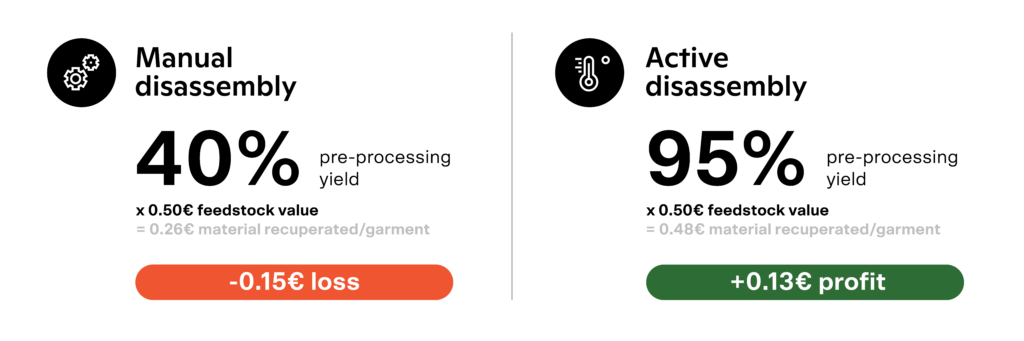
With eco-design solutions such as Resortecs, the disassembly or “de-stitching” of garments is automated, allowing for the elimination of trims and the separation of two different textiles in reusable fractions with an average material recuperation rate of 95%. This pre-processing technology not only facilitates the recycling of complex/multilayer textile products, such as denim, jackets and swimwear, but also roughly doubles the post-consumer textile recycling yields.
Despite the widespread recognition of the crucial role yields play, it is surprising how little emphasis is placed on discussions regarding efficiencies and productivity at annual textile circularity and recycling conferences. Similar to the semiconductor industry in the 1990s, prioritising yields is imperative when deciding on which technologies and processes to integrate. By increasing the pre-processing and recycling yields we will be able to industrialise textile-to-textile recycling and achieve price-competitive sustainable materials for the textile industry.
In conclusion, the journey towards mainstream textile-to-textile recycling hinges on maximising process yields and optimising efficiency across the value chain. As described above, an optimised eco-design has a significant impact on the recycling process yields and thus largely affects the price of recycled content textile brands have to pay to be compliant. This insight highlights an opportunity for textile players to switch from a reactive to proactive approach: brands must take action in the way their garments are designed to ensure low price recycled feedstock, leading to less compromise on their margins in the long-term.
By addressing pre-processing challenges and leveraging eco-design technologies like Resortecs, the industry can pave the way for price-competitive sustainable materials and drive the transition towards a circular economy in the textile sector.
Author: Cédric Vanhoeck, CEO at Resortecs
Resortecs policy asks Waste Framework Directive revision
1. Swift introduction of mandatory and harmonised Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes for textile products across the EU to introduce their separate collection.
2. Extended Producer Responsibility fees should be eco-modulated to incentivise producers to ecodesign their products. Design for disassembly must be included as a criterion.
3. Include a 2030 target for textiles-textiles recycling target as well as a fibre-to-fibre sub-target (for when the former is no longer an option to avoid premature downcycling). These targets should increase over time.
4. To deliver the waste hierarchy principles in practice, recognition and support of so-called pre-recycling techniques that are preconditions to effective circularity operations, such as sorting and disassembly, should be developed and integrated into the modernised Waste Framework Directive.
____________________________________________________________________
Action to make circular economy the norm is urgent. The Circularity Gap Report 2023 demonstrates that the world’s circularity has declined from 9.1% to 7.2% over the past five years, whilst total material extraction has almost doubled since 2000, reaching 100 billion tonnes today. As recognised by the EU Green Deal, the Circular Economy Action Plan, the EU Industrial Strategy, and the Textiles Ecosystem Transition Pathway, the textiles sector is key to the green transition as it is the fourth most resource intense industry, it accounts for 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, and less than 1% of all textiles waste collected enters into a circular loop.
Resortecs supports the European Commission’s 2030 vision for a competitive, resilient, and innovative textiles sector laid out in the EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles, particularly that all textile products placed on the EU market are eco-designed, sustainable and with producers taking responsibility for their products along the value chain with sufficient capacities for recycling and ending incineration and landfilling.
To achieve this ambitious vision, Europe must unlock industrial-scale circularity for textiles. Design for disassembly is key to unleash the full potential of textile-to-textile reuse, repair, and recycling. Even with an ideal circularity infrastructure, most textile products on the market would remain too complex or expensive to repair or recycle once they become waste because they are not designed for disassembly and, therefore, circularity. Once collected, most cannot be processed without a pre-recycling step such as disassembly. This is a key end-of-life-problem for the industry. For example, over 78% of all textile products are multi-material and the presence of zippers and trims like elastic bands hinder recycling. This results in material loss as most textile waste goes to incineration or landfill, and most new textiles products manufactured from scratch.
Disassembly is still a manual and costly process. To address this, Resortecs’ active disassembly innovations – a range of heat-dissolvable threads (‘Smart Stitch™’) and thermal disassembly system (‘Smart Disassembly™’) – helps to replace textiles designed for waste with textiles eco-designed for disassembly, thereby enabling material recovery for reuse, repair, upcycling, and high-quality recycling as well as waste prevention. Active Disassembly represents the pinnacle of Design for Disassembly methodologies (other pre-recycling available today include mechanical disassembly and manual disassembly). By incorporating releasable fasteners in a product’s design and assembly – such as Resortecs’ SmartStitch™ – active disassembly delivers an automatic, non-destructive, and economic industrial disassembly process that segregates components and materials of a product at its end-of-life.
A major benefit of Resortecs is that it acts as a drop-in solution to the textiles value chain as no significant infrastructure or manufacturing changes are needed in the value-chain for implementation of this technology. It also delivers circularity without compromising the creativity, design, and quality of clothing.
Click here or on the image below to download the full position paper.

Join us.
Subscribe to our newsletter.
By subscribing, I agree with having my personal data stored and processed by Resortecs so I can receive future updates and marketing offers.
